Once you have a domain with wordpress installed you need our wordpress tutorials for beginners. Here you will understand how to customise your website and manage your digital business in general. Lets understand each thing, one by one.
What is WordPress?
- An open-source content management system (CMS) popularly used for creating websites, blogs, and ecommerce stores.
- Highly customizable with themes and plugins.
- Codebase is written in PHP and uses a MySQL database.
Differences between WordPress.com and WordPress.org
- WordPress.org:
- Open Source Self-hosted CMS solution
- Requires purchasing hosting and domain name.
- Full control over customization and code.
- Access to all themes and plugins, including third-party options.
- WordPress.com:
- Free plan has Limited customization options.
- Paid service by wordpress. Creator plan costs 300$ annually
Benefits of Using WordPress Open Source CMS
- User-Friendly:
- Easy to use, even for beginners.
- Intuitive interface for content creation and management.
- Customizable:
- Thousands of themes and plugins available.
- Ability to modify code for advanced customization.
- SEO-Friendly:
- Built-in SEO features.
- Support for SEO plugins to enhance optimization.
- Responsive Design:
- Many themes are mobile-friendly.
- Ensures a good user experience across devices.
- Community Support:
- Large, active community for support and resources.
- Extensive documentation and tutorials available.
- Scalable:
- Suitable for small blogs to large enterprise websites.
- Can handle high traffic and complex functionalities.
- Security:
- Regular updates for security enhancements.
- Availability of security plugins to protect sites.
- Cost-Effective:
- Free to use, with optional paid plugins and themes.
- Lower development costs compared to building a site from scratch.
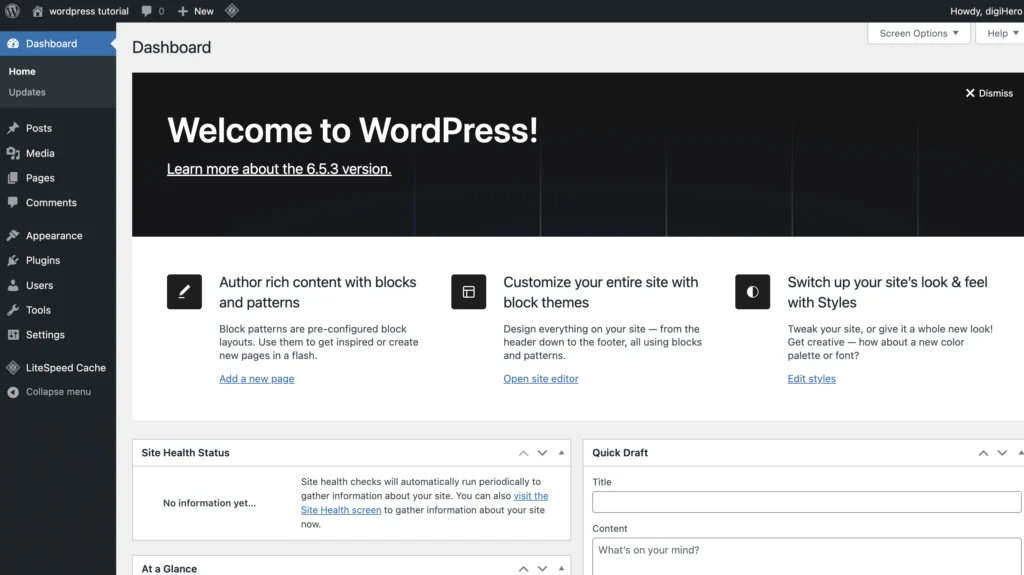
Understanding the WordPress Dashboard
Overview of the Dashboard
- Introduction:
- Central control panel for managing a WordPress site.
- Provides quick access to essential site management features.
- Main Components:
- Welcome Panel: Overview and quick links to get started.
- At a Glance: Summary of posts, pages, comments, and WordPress version.
- Activity: Recent posts, comments, and site activity.
- Quick Draft: Create a quick draft post.
- WordPress News: Latest news and updates from the WordPress community.
Navigation Menu
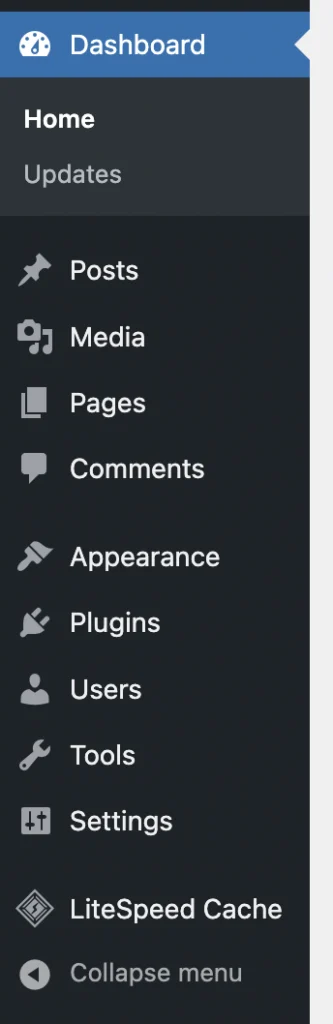
- Location:
- Located at the left side of the dashboard.
- Contains links to all administrative functions.
- Main Sections:
- Dashboard: Home and updates overview.
- Posts: Add, edit, and manage blog posts.
- Media: Inbuilt library for managing media files like images and videos.
- Pages: Add, edit, and manage static pages.
- Comments: Moderate and manage user comments.
- Appearance: Customize themes, menus, widgets, and other appearance settings.
- Plugins: Install, activate, deactivate, and manage plugins.
- Users: Manage user accounts and roles.
- Tools: Access to import/export tools and site health.
- Settings: General, writing, reading, discussion, media, and permalinks settings.
- Customizing WordPress Navigation menu:
- Plugins can add new menu items or submenus.
Admin Toolbar
- Location:
- Appears at the top of the dashboard and front-end when logged in.
- Main Functions:
- WordPress Logo: Links to WordPress.org, documentation, support forums.
- Site Name: Links to the front-end of the site.
- Updates: Notifications about available updates for WordPress, themes, and plugins.
- Comments: Quick access to manage recent comments.
- New: Quick links to create new posts, media, pages, or users.
- Edit Post/Page: Direct link to edit the current post/page when viewing the front-end.
- User Profile: Access to user profile and logout.
- Customization:
- Can be customized by themes and plugins to add additional links and functionality.
Configuring WordPress Settings
General Settings
- Site Title:
- Name of your site; appears in the title bar and browser tab.
- Tagline:
- Short description of your site; appears under the site title.
- WordPress Address (URL):
- URL where your WordPress files are installed.
- Site Address (URL):
- URL visitors will use it to reach your site.
- Email Address:
- Administrative email address for notifications.
- Membership:
- Allow anyone to register (yes/no).
- New User Default Role:
- Default role assigned to new users (e.g., Subscriber, Contributor).
- Timezone:
- Set your site’s timezone.
- Date Format:
- Choose how dates are displayed.
- Time Format:
- Choose how times are displayed.
- Week Starts On:
- Select the start day of the week.
Writing Settings
- Default Post Category:
- Category assigned to posts if no other category is specified.
- Default Post Format:
- Default format for posts (e.g., Standard, Aside).
- Post via Email:
- Settings for publishing posts via email (requires specific email account setup).
- Update Services:
- List of services to notify when you publish a new post.
Reading Settings
- Your Homepage Displays:
- Choose between displaying the latest posts or a static page.
- If there is a static page, select the homepage and posts page.
- Blog Pages Show at Most:
- Number of posts displayed per page.
- Syndication Feeds Show the Most Recent:
- Number of items displayed in RSS feeds.
- For Each Article in a Feed, Show:
- Display full text or summary in feeds.
- Search Engine Visibility:
- Option to discourage search engines from indexing the site.
Discussion Settings
- Default Article Settings:
- Do Allow link notifications (pingbacks and trackbacks) from other blogs .
- Do Allow people to submit comments on new posts.
- Other Comment Settings:
- Require name and email.
- Optional for Users to be registered and logged in to comment.
- Uncheck Automatically close comments on older posts.
- Email Me Whenever:
- Email notifications for comments and moderation.
- Before a Comment Appears:
- Comments must be manually approved.
- The author who made the comment must have a previously approved comment.
- Comment Moderation:
- Settings for holding comments in the moderation queue.
- Comment Blacklist:
- Keywords to mark comments as spam.
- Avatars:
- Enable avatars and choose default avatar settings.
Permalink Settings
- Common Settings:
- Choose the URL structure (e.g., Plain, Day and name, Month and name, Numeric, Post name, Custom Structure).
- Optional Settings:
- Custom URL bases for category and tag archives.
Other Important Settings
- Media Settings:
- Image Sizes: Define dimensions for thumbnail, medium, and large images.
- Uploading Files: Choose whether to organize uploads into month- and year-based folders.
- Privacy Settings:
- Privacy Policy Page: Set and edit the privacy policy page.
- Reading Settings (additional):
- Homepage Settings: Choose a static page or latest posts for the homepage.
By configuring these settings, you can ensure your WordPress site operates smoothly and is tailored to your preferences.
WordPress User Management
Adding and Managing Users
- Adding New Users:
- Go to Users > Add New in the WordPress Dashboard.
- Enter the new user’s details: Username, Email, First Name, Last Name, Website (optional), and Password.
- Select a user role from the dropdown menu.
- Optionally, send the new user an email about their account.
- Click on Add New User to create the user account.
- Managing Existing Users:
- Navigate to Users > All Users to view all registered users.
- Edit user details by clicking Edit under the user’s name.
- Change user roles, reset passwords, or update personal information.
- Delete users by selecting the checkbox next to their name and choosing Delete from the bulk actions dropdown.
User Roles and Permissions
- Administrator:
- Full access to all settings, content, and site management.
- Can add, edit, and delete content, install plugins, manage themes, and add or remove users.
- Editor:
- Can manage and publish posts and pages, including those created by other users.
- Can moderate comments and manage categories and tags.
- Author:
- They can write, or edit, or publish their own posts.
- Cannot manage posts by other users.
- Contributor:
- They can write or edit their own posts but cannot publish those posts.
- Submissions need approval by an Editor or Administrator.
- Subscriber:
- Can only manage their own profile.
- Primarily used for users who need access to comment or view restricted content.
Best Practices for User Management
- Limit Administrator Access:
- Only grant Administrator access to trusted individuals.
- Reduce the risk of accidental or malicious site changes.
- Use Strong Passwords:
- Use strong, unique passwords. Never use admin as username or password
- Consider using a password manager for better security.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
- 2FA adds an extra layer of security for user accounts.
- Use plugins like Two Factor or WP 2FA to enable 2FA.
- Regularly Review User Roles:
- Periodically review user roles and permissions.
- Ensure users have appropriate access levels.
- Monitor User Activity:
- Use plugins like Simple History to track user activities.
- Monitor login attempts, content changes, and user management actions.
- Educate Users:
- Provide training or guidelines on proper site usage.
- Ensure users understand their roles and responsibilities.
- Backup User Data:
- Regularly back up the database to safeguard user data.
- Use reliable backup solutions like UpdraftPlus or BackupBuddy.
- Remove Inactive Users:
- Periodically clean up inactive or obsolete user accounts.
- Reduce security risks associated with unused accounts.
By following these best practices and properly managing user roles and permissions, you can maintain a secure and efficiently managed WordPress site.
Customising Appearance and Managing Plugins are in Next Part of this guide
Customising Appearance: WordPress Tutorials for beginners Part 2